
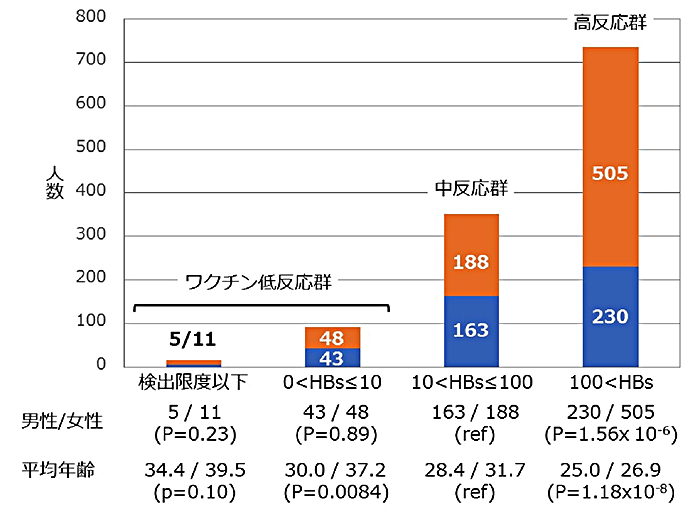
Approximately 5-10% of individuals, who are vaccinated with a hepatitis B (HB) vaccine designed based on the HBV genotype C, fail to acquire protective levels of antibodies. Here, host genetic factors behind low immune response to this HB vaccine were investigated by a genome wide association study (GWAS) and HLA association tests. A GWAS and HLA association tests were carried out using a total of 1,193 Japanese individuals including 107 low responders, 351 intermediate responders, and 735 high responders. Classical HLA class II alleles were statistically imputed using the genome-wide SNP typing data. The GWAS identified independent associations of HLA-DRB1-DQB1, HLA-DPB1 and BTNL2 genes with immune response to a HB vaccine designed based on the HBV genotype C. Five HLA-DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes and two DPB1 alleles showed significant associations with response to the HB vaccine in a comparison of three groups of 1,193 HB vaccinated individuals. When frequencies of DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes and DPB1 alleles were compared between low immune responders and HBV patients, significant associations were identified for three DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes, and no association was identified for any of the DPB1 alleles. In contrast, no association was identified for DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes and DPB1 alleles in a comparison between high immune responders and healthy individuals. The findings in this study clearly show the importance of HLA-DR-DQ (i.e. recognition of a vaccine related HB surface antigen (HBsAg) by specific DR-DQ haplotypes) and BTNL2 molecules (i.e. high immune response to HB vaccine) for response to a HB vaccine designed based on the HBV genotype C. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
GWAS; HBV; Vaccine; host genetic factors

大约5-10%接种了基于HBV基因型C设计的乙肝(HB)疫苗的个体未能获得抗体保护水平。在此,通过全基因组关联研究(GWAS)和HLA关联测试研究了针对该HB疫苗的低免疫应答背后的宿主遗传因子。使用总共1,193名日本人进行GWAS和HLA关联测试,其中包括107名低应答者,351名中间应答者和735名高应答者。使用全基因组SNP分型数据统计推断经典HLA II类等位基因。GWAS鉴定了HLA-DRB1-DQB1,HLA-DPB1和BTNL2基因与针对基于HBV基因型C设计的HB疫苗的免疫应答的独立关联。5个HLA-DRB1-DQB1单体型和2个DPB1等位基因显示与HB疫苗的反应显着相关,在三组1,193HB接种疫苗的个体中进行比较。当比较低免疫反应者和HBV患者中DRB1-DQB1单倍型和DPB1等位基因的频率时,三种DRB1-DQB1单倍型鉴定出显着相关性,并且没有发现任何DPB1等位基因的关联。相比之下,在高免疫应答者与健康个体之间的比较中未鉴定DRB1-DQB1单倍型和DPB1等位基因的关联。该研究中的发现清楚地显示了HLA-DR-DQ(即通过特异性DR-DQ单元型识别疫苗相关的HB表面抗原(HBsAg))和BTNL2分子(即 对HB疫苗的高免疫应答)对基于HBV基因型C设计的HB疫苗的应答。本文受版权保护。版权所有。
GWAS; HBV; 疫苗; 宿主遗传因素
| 欢迎光临 肝胆相照论坛 (http://hbvhbv.info/forum/) | Powered by Discuz! X1.5 |