肝胆相照论坛
标题: 一个 博客评论GS9620&ARC520 [打印本页]
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-3 14:09 标题: 一个 博客评论GS9620&ARC520
Saturday, November 2, 2013 Gilead Lead Chronic HepB Candidate GS-9620 Conceived as a More Patient-Friendly Interferon

As I was reading the latest PK-PD study by Gilead on its lead experimentalchronic HepB drug candidate GS-9620 (Fosdick et al. 2013), itfinally dawned on me that much-touted GS-9620 has been designed to be nothing more than abetter tolerated, more convenient version of an already existing treatmentoption, recombinant interferon. GS-9620is therefore an example of the typical incrementalist Big Pharma value creation strategy. By contrast, if successful, an HBsAgknockdown approach such as with Arrowhead’s ARC520 would bring to healthcareproviders and patients an entirely new, desperately needed treatment option asthe field has become stuck with interferons and RT inhibitors for years.
GS-9620 checks a numberof boxes for an interferon-better
Interferons for the treatment of chronic HepB and HepC is widely regarded as a mixedblessing. In light of its very poortolerability, including flu-like symptoms and depression, patients often opt not to be potentially cured instead of suffering through a year or soof feeling just miserable. Of course, it does not helpthat after all this, the prospects of a (functional) cure still remain depressinglylow in the case of HepB, on the order of 10% for the gold standard HBsAg seroconversion.
Gilead is developing the orally administered, small moleculetoll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) agonist GS-9620 in order to provoke naturalinterferon production along the GI-liver axis without causing systemicexposures with interferon. It is the systemic, body-wide actions of interferon that are responsiblefor its poor tolerability.
This is supported by the PK-PD data in Fosdick et al. that show that while GS9620 isefficiently taken up in the GI tract, it does not make it out of the liver into the systemic circulation. Moreover, despite local interferon production somewhere along the GI-liver tract, interferon itself seems to be largely contained locally as long asthere has not been too much stimulation. Accordingly, it should be possible to get some of the beneficial interferoneffects where it is needed (the liver) without the detrimental systemicexposure.
As a TLR7-specific agonist, GS9620 is also thought to avoidtriggering the type of pro-inflammatory cytokines that you might expect fromTLR activation. In particular, you would wantto steer clear of TNF-alpha to avoidtissue damage and hypersensitivity reactions. Indeed, TNF-alpha is hardly induced in monkeys and humans.
On a related note, the data supporting that TLR7-agonism atleast in primates should specificallyinduce interferon and not TNF-alpha is also good news to efforts aiming tocombine TLR agonism and RNAi gene knockdown as RNA is the natural ligand forTLR7. I do not predict that this willhappen, nor suggest that Arrowhead (or Tekmira) should go down that route, but you couldimagine a modified ARC520 with intentional TLR7 agonism, thus combining the two anti-HBV mechanisms.
Human studies suggestnarrow therapeutic window
While the theory behind GS-9620 is attractive and thepreclinical data apparently supportive of it, the clinical experience thus farsuggests that the development of GS-9620 will not be an easy one. In particular, at least 2mg of the drug wererequired to be able to detect two sensitive biomarkers for interferonproduction, OAS1 and MX1 (Lopatin et al. 2013). The assumptionhere is that you need to be able to observe OAS1 and MX1 in order to have aninterferon benefit in the liver.
However, as doses were escalated, systemic interferon wasdetected in the trial subjects starting at 8mg and coincided with the expected sideeffects. This means that thetherapeutic index for GS-9620 may be as narrow as 2-6mg. Considering not only the inter-species, butalso the considerable intra-species variability of TLR biology in humans, itremains to be seen whether the therapeutic window will be narrowing evenfurther following large multi-national studies.
More value forinnovation
Ultimately, I do feel that GS-9620 may incrementally enhance the treatment experience for chronic HepBpatients: increased tolerability and convenience (oral vs injectable), butlikely only slightly increased cure rates due to improved compliance. This would certainly justify a price tagexceeding that of current interferons. However, when comparing it to an agent like ARC520 which could transform the treatment of chronic HepB, it is difficult to see how the two agents would bepriced at the same level.
The issue is not just limited to cost, but extends topotential regulatory incentives, including accelerated approval andbreakthrough designation. Don’t expectan orphan designation for a chronic HepB drug though!
And from a business development perspective, just theability alone of ARC520 to rapidly and profoundly down-regulate HBsAg shouldmake it an attractive candidate to be paired with other HepB agents, includingGilead’s GS-9620.
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-3 14:10
2013年11月2日(星期六)
Gilead公司铅的慢性乙肝候选人GS - 9620设想为更多患者友好干扰素
因为我读的PK - PD的最新研究由吉利德铅的实验性慢性乙肝的候选药物GS - 9620 (福斯迪克等, 2013) ,终于醒悟过来了,备受吹捧的GS -9620设计已经是没什么更多比耐受性更好,更方便的版本已经存在的治疗选项,重组干扰素。因此, GS - 9620是典型的渐进主义的大型制药企业的价值创造战略的一个例子。相比之下,如果成功的话,如带箭头的ARC520的乙肝表面抗原敲除的方法会带来一个全新的医疗保健提供者和患者,迫切需要治疗的选择,因为该领域已成为套牢干扰素和逆转录酶抑制剂多年。
GS - 9620检查一些箱子干扰素更好
干扰素治疗慢性乙肝和HEPC被广泛视为是喜忧参半。鉴于其耐受性差,包括流感样症状和抑郁症,患者往往选择可能并非治愈,而不是通过一年半载的感觉只是惨的痛苦。当然,这并没有帮助,毕竟这一个(功能)治愈前景仍然令人沮丧的低乙肝疫苗的情况下, 10%为黄金标准的乙肝表面抗原血清学转换的顺序。
Gilead公司开发的口服小分子Toll样受体7 ( TLR7 )激动剂GS- 9620 ,以便挑起沿胃肠肝轴与干扰素,而不会造成系统性风险的天然干扰素生产。它是全身性的,全身性的行动干扰素,负责其耐受性差。
这是支持的PK - PD数据福斯迪克等。表明, ,而GS9620有效地在胃肠道,它不会做出来的肝脏进入全身循环。此外,尽管本地干扰素生产某处胃肠肝道,干扰素本身似乎在很大程度上包含只要本地并无太大的刺激。因此,它应该是可以得到一些有益的干扰素效果需要的地方(肝脏)无有害全身暴露。
作为一个的TLR7特定激动剂, GS9620也被认为是避免引发促炎症细胞因子的类型,你可能期望从TLR激活。特别是,你会想避开肿瘤坏死因子-α ,以避免组织损伤和过敏反应。事实上,几乎不诱导在猴子和人肿瘤坏死因子-α 。
在一个相关的说明,数据支持, TLR7激动,至少在灵长类动物特异性诱导干扰素和TNF -α是努力TLR激动和RNAi基因敲除结合RNA是TLR7的天然配体也是一个好消息。我不预测,这将发生,也不表明箭头(或TEKMIRA )应该走这条路线,但你能想象修改ARC520故意TLR7激动,因此结合这两种抗乙肝病毒机制。
人类的研究表明,治疗窗窄,
虽然GS - 9620背后的理论是有吸引力的,它的临床前数据显然支持,迄今临床经验表明, GS - 9620的发展不会是轻松的一年。特别是,至少2mg的药物必须是能够检测到两个敏感的生物标志物用于生产干扰素, OAS1和MX1 (洛帕廷等人2013年) 。这里的假设是,你需要能够观察到OAS1和MX1在肝脏中有一个干扰素利益。
然而,由于剂量上升,全身干扰素检测在试验对象开始在8毫克,正好与预期的副作用。这意味着,治疗指数为GS - 9620 2 - 6毫克可以窄。不仅考虑跨品种,而且还相当的种内变异的TLR在人类生物学,治疗窗是否会进一步收窄甚至大型跨国研究,仍有待观察。
更多的创新价值
最后,我觉得, GS - 9620可能会逐步提高对慢性乙肝患者的治疗经验:增加耐受性和方便(口服和注射) ,但可能仅略有增加治愈率,由于更好地遵守。这肯定会证明一个明码标价超过电流干扰素。然而,当比较ARC520剂如可能改变治疗慢性乙肝,这是很难看,这两种药物如何定价将在同一水平。
问题并不仅仅局限于成本,而是延伸到潜在的监管激励措施,包括加速批准,并突破指定。不要指望指定为慢性乙肝的药物虽然是个孤儿!
从业务发展的角度来看,只是单独的能力ARC520迅速和深刻下调的HBsAg应该让一个有吸引力的候选人进行配对与其他乙肝药物,包括Gilead公司的GS - 9620 。
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-3 14:13
About Me[博客]
Dirk Haussecker
Services provided: • Scientific due diligence on RNAi trigger designs and delivery technologies, both synthetic and DNA-directed; • Scientific due diligence on microRNA agonist/antagonist designs and delivery, both synthetic and DNA-directed; • Competitive analysis of RNAi-related technologies and companies in the space; • Formulating RNAi Therapeutics business development strategies; • RNAi-related scientific writing targeted at investors; • Reports from scientific conferences. Who might benefit: -RNAi Therapeutics companies; - biotech/pharma companies interested in entering RNAi Therapeutics development; -investors in RNAi-related opportunities. Please send enquiries to: dirk (dot) haussecker (at) gmail (dot) com About Me: Until 2009 a post-doc at Stanford University, I have been involved in RNAi-related research for over 9 years and am excited about the therapeutic prospects of this technology. I currently work as a freelance RNAi Therapeutics analyst/consultant, based on science, aware of the markets.
关于我
德克Haussecker的
提供的服务: • RNAi的触发设计和交付技术,合成和DNA指导的科学尽职调查; •科学的microRNA激动剂/拮抗剂的设计和交付尽职调查,合成和DNA指导; RNAi相关的技术竞争分析公司在空间; •制定RNAi疗法的业务发展策略; RNAi相关的科学写作针对投资者•从科学会议的报告。谁可能受益: RNAi疗法公司 - 生物技术/制药公司有意进入RNAi疗法的发展;投资者在RNAi相关的机会。请查询寄往:德克(点) haussecker ( AT )的Gmail (点)的COM关于我:直到2009年在斯坦福大学的博士后,我一直参与RNAi相关的研究超过9年,并感到兴奋治疗这项技术的前景。我目前的工作作为一个自由RNAi疗法分析师/顾问,以科学为基础,了解市场。
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-3 14:19
本帖最后由 StephenW 于 2013-11-3 14:19 编辑
请注意:
德克 Haussecker博士是箭头公司的投资者。他不是一个医生。他是一个RANIi专家。
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-3 14:46
虽然没有对这两个药物有深入的了解,不过感觉还是有希望的,520这个药物估计还是rep9ac更快一点吧,这个我也想了一个问题,为何rep9ac的实验结果并不尽如人意,为什么rep9ac的下一步实验是和恩替联用的呢?这其实已经说明了问题,虽然表抗的抑制作用可以暂时性解除,但病毒并不会轻易就范。要知道,大量病毒在细胞内是以整合dna的形式存在的,更不要说cccdna了,这就是可怕之处,整合dna先不要怕,如果可以产生抗体。整合就整合了,没什么大不了的。但cccdna呢,这个东西极其活跃,不容易消除,我的推断是在启动了人体的某种免疫反应后,会出现一种特异性或非特异性的干扰素,具体是什么,人类还未分离出来,估计很难分离。所以,rep9ac虽然可以解除免疫抑制,但人体内的免疫反应是否能够持续那么久,那么强,来完全消灭cccdna,这个就不好说了。我的看法是,肯定有一些人无法消除。因为乙肝这个病毒已经和人类同化了。如果人类不治疗,几十万年后,乙肝也能被人体吸收为无害病毒,因为相处了太久,彼此进化出了和平共处的机制了。比如黑猩猩携带了艾滋病毒,但没有发病,也不产生什么严重后果,应该也是同化的结果。但其实这一类人,你治疗不治疗,也不是什么特别大的问题,至少从短期来看,没有特别需要治疗的感觉。
但我们的目标是彻底解除乙肝的威胁,希望能够更快更好的清楚病毒,再谈rep9ac联用的问题,恩替固然很好,但我觉得关键还是需要抑制cccdna的药物,阿的平应该有这样的效果。但是临床上的东西,操作起来估计还是不容易下结论的。
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-3 15:31
本帖最后由 StephenW 于 2013-11-3 15:32 编辑
回复 齐欢畅2 的帖子
首先,我想补充一些贵点:
1. "520这个药物估计还是rep9ac更快一点吧"
可能. 它们是不同的. Rep9AC 不抑制Dane颗粒(HBV病毒粒子)的生产和释放.
Dane颗粒大衣是乙肝表面抗原. ARC520 抑制HBsAg的生产, 因此,也可能抑制Dane颗粒的生产(没有生产,没有释放).
2."为何rep9ac的实验结果并不尽如人意"
rep9ac的实验结果非常好,但少数病人,没有足够的细节.
3. "为什么rep9ac的下一步实验是和恩替联用的呢?"
我的猜测,有些患者有病毒载量,恩替卡韦/替诺福韦将降低病毒载量,这应该有帮助.
4. "虽然表抗的抑制作用可以暂时性解除,但病毒并不会轻易就范。"
很重要的一点,甚至当乙肝表面抗原阴性,HBsAb阳性,HBVDNA检测不到,一些cccDNA的仍然存在.
5. "大量病毒在细胞内是以整合dna的形式存在的"
根据我的理解,不是整个cccDNA的嵌入到我们的DNA,只有小块,这样的一个小块可能包含产生乙肝表面抗原的基因.
6. "我的推断是在启动了人体的某种免疫反应后,会出现一种特异性或非特异性的干扰素,具体是什么"
根据我的理解, 是干扰素Gamma. 整个免疫是非常复杂的,我不知道和理解.
7. "但人体内的免疫反应是否能够持续那么久,那么强,来完全消灭cccdna,这个就不好说了。"
同意,但可以控制. 这是为什么,你已经清除病毒后,当你使用药物将降低你的免疫系统,你应该再次服用抗病毒药,作为一项预防措施.
8. "但我觉得关键还是需要抑制cccdna的药物,阿的平应该有这样的效果"
阿的平没有临床试验中,没有证据.
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-3 17:44
回复 StephenW 的帖子

作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-3 18:00
1. "520这个药物估计还是rep9ac更快一点吧"
可能. 它们是不同的. Rep9AC 不抑制Dane颗粒(HBV病毒粒子)的生产和释放.
Dane颗粒大衣是乙肝表面抗原. ARC520 抑制HBsAg的生产, 因此,也可能抑制Dane颗粒的生产(没有生产,没有释放).
-----抑制hbsag的产生,那非常好啊。
2."为何rep9ac的实验结果并不尽如人意"
rep9ac的实验结果非常好,但少数病人,没有足够的细节.
----曾经看到过实验的一些数据,确实很不错,但那些是短期数据,长期数据,我没有看到过。
3. "为什么rep9ac的下一步实验是和恩替联用的呢?"
我的猜测,有些患者有病毒载量,恩替卡韦/替诺福韦将降低病毒载量,这应该有帮助.
-----长期实验数据,我觉得未必就非常乐观,为什么联用恩替?如果效果非常好的话,不需要联用恩替了。这一点应该是可以肯定的。
4. "虽然表抗的抑制作用可以暂时性解除,但病毒并不会轻易就范。"
很重要的一点,甚至当乙肝表面抗原阴性,HBsAb阳性,HBVDNA检测不到,一些cccDNA的仍然存在.
-----------是的。病来如山倒,病去如抽丝,何况是在分子水平的抽丝。生物学都已经进化到量子生物学了,复杂程度远非我们大脑可以接受的地步。
5. "大量病毒在细胞内是以整合dna的形式存在的"
根据我的理解,不是整个cccDNA的嵌入到我们的DNA,只有小块,这样的一个小块可能包含产生乙肝表面抗原的基因.
------整合dna应该是没有问题的,但它可以复制出cccdna,所以理论上有复发的可能。但据我了解的情况看,真的治愈的乙肝患者,很少有复发的。
6. "我的推断是在启动了人体的某种免疫反应后,会出现一种特异性或非特异性的干扰素,具体是什么"
根据我的理解, 是干扰素Gamma. 整个免疫是非常复杂的,我不知道和理解.
-----伽马干扰素,如果是这个的话,那就好办了,但事实上,伽马干扰素是很重要的干扰素,但并不是唯一重要。肯定还存在其他,特异或非特异的免疫物质。
7. "但人体内的免疫反应是否能够持续那么久,那么强,来完全消灭cccdna,这个就不好说了。"
同意,但可以控制. 这是为什么,你已经清除病毒后,当你使用药物将降低你的免疫系统,你应该再次服用抗病毒药,作为一项预防措施.
-------控制是思路,但如何控制。我曾经研究过这个问题,提出了一个免疫接力的理论,但没有办法试试。
8. "但我觉得关键还是需要抑制cccdna的药物,阿的平应该有这样的效果"
阿的平没有临床试验中,没有证据.
------阿的平有非特异性的抗病毒作用,理论上可以抑制cccdna,实验数据也有,但是是未发表的,所以,的确没有证据。
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-3 18:36
本帖最后由 StephenW 于 2013-11-3 18:42 编辑
回复 齐欢畅2 的帖子
1)------整合dna应该是没有问题的,但它可以复制出cccdna,所以理论上有复发的可能。但据我了解的情况看,真的治愈的乙肝患者,很少有复发的。
cccDNA的不能简单自我复制。cccDNA-->转录-->翻译 -- >病毒蛋白+前基因组(pgRNA) - >反转录 - >形核衣壳-->进入细胞核>释放hbvDNA-->形成cccDNA的.
cccDNA太大,不能完全嵌入在我们的DNA. (我的理解).
2)但如何控制
乙肝表面抗体停止再感染, CD8+T细胞杀死/控制仍然感染细胞.
3)阿的平有非特异性的抗病毒作用,理论上可以抑制cccdna,实验数据也有,但是是未发表的
"未发表的" - 意味着不存在.
"实验数据" - 试管(test tube)或人,非常大的不同
作者: 咬牙硬挺 时间: 2013-11-3 21:04
感谢分享
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-3 21:45
还是比较期待rep9ac,不知何时有结果。
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-13 00:33
http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01103
Pharmacology
Indication For the treatment of giardiasis and cutaneous leishmaniasis and the management of malignant effusions.
Pharmacodynamics Quinacrine has been used as an antimalarial drug and as an antibiotic. It is used to treat giardiasis, a protozoal infection of the intestinal tract, and certain types of lupus erythematosus, an inflammatory disease that affects the joints, tendons, and other connective tissues and organs. Quinacrine may be injected into the space surrounding the lungs to prevent reoccurrence of pneumothorax. The exact way in which quinacrine works is unknown. It appears to interfere with the parasite's metabolism.
Mechanism of action The exact mechanism of antiparasitic action is unknown; however, quinacrine binds to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in vitro by intercalation between adjacent base pairs, inhibiting transcription and translation to ribonucleic acid (RNA). Quinacrine does not appear to localize to the nucleus of Giaridia trophozoites, suggesting that DNA binding may not be the primary mechanism of its antimicrobial action. Fluorescence studies using Giardia suggest that the outer membranes may be involved. Quinacrine inhibits succinate oxidation and interferes with electron transport. In addition, by binding to nucleoproteins, quinacrine suppress the lupus erythematous cell factor and acts as a strong inhibitor of cholinesterase.
Absorption Absorbed rapidly from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration.
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-13 00:38
Quinacrine intercalation DNA
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-13 18:37
回复 齐欢畅2 的帖子
[url=http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/File NA_intercalation.jpeg]
NA_intercalation.jpeg]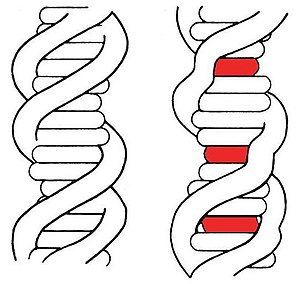 [/url]
[/url]
[url=http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/File NA_intercalation.jpeg]
NA_intercalation.jpeg] [/url]
[/url]
發生於圖中紅色區域的嵌入作用使DNA長鏈扭曲變形。
嵌入(英語:Intercalation,或譯插層)在化學上是指在兩個分子或基團之間加入一個分子,過程可逆。例如DNA嵌入與石墨嵌入化合物(graphite intercalation compound)。
DNA嵌入[编辑]有許多分子可與生物體內的DNA發生交互作用,以配體為例,嵌入是配體分子與DNA的一種結合方式,當配體大小符合鹼基對之間的空隙時,就有可能發生嵌入。通常嵌入DNA的配體是多環類、芳香類,或是平面分子。常見的例子包括溴化乙錠、原黃素(proflavine)、道諾霉素(daunomycin)、阿黴素(doxorubicin)、沙利竇邁(thalidomide)等。這些物質可應用於化學治療,抑制癌細胞的生長。
參見[编辑]
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-13 19:03
我不了解任何有关插层进入DNA. 如果Quinacrine插入到cccDNA的,它可能会抑制cccDNA的转录. 但如果它插进入肝细胞,肾细胞,心脏细胞.....的dna ...当细胞分裂时,它会防止DNA 复制.杀死这些细胞,并引起副作用?
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-13 20:19
值得研究。
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-13 20:22
人的dna比cccdna要稳定得多,而且细胞的周期寿命比较长。
cccdna其实是不稳定的,它不断的解旋进行复制,是动态的平衡。
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-16 15:38
Monday, November 4, 2013 ARC520 for Chronic HepB: The Immune System…It’s Reactivating!
 Usually, immune stimulation which manifest itself as flu-like symptoms and the like is something that you do not want to see with an RNAi Therapeutic. Having said that, there are settings in which you want to see immune stimulations. This is also the case for the treatment of chronic HBV with a HBsAg knockdown approach.
Usually, immune stimulation which manifest itself as flu-like symptoms and the like is something that you do not want to see with an RNAi Therapeutic. Having said that, there are settings in which you want to see immune stimulations. This is also the case for the treatment of chronic HBV with a HBsAg knockdown approach.
ARC520 is the lead candidate in this effort and yesterday the sponsor, Arrowhead Research, presented very exciting data in a chronically infected chimpanzee that had been treated with the RNAi agent. The data are not only exciting because they presumably represent the fastest reduction of the HBsAg antigen ever seen in a real infection (note: only the chimpanzee is thought to reflect human HBV infection), no, what is even more exciting is that the data are consistent with a HBsAg-specific T-cell immune response.
As the success of an HBsAg knockdown approach for the treatment of chronic HBV hinges on the hypothesis that by knocking down HBsAg it might be possible for the body to re-activate an adaptive immune response against the virus, the data in my mind are the biggest de-risking event in the development of ARC520.
The data
At the 2013 Liver Meeting of the AASLDin Washington DC, Arrowhead Research presented more detailed data on the chimpanzee that had been treated with ARC520. Before that we had knownthat two doses of ARC520 (one of 2.0mg/kg and one of 3.0mg/kg) spaced 14 days apart was able to knock down HBsAg by ~80%, HBeAg by over 90%, and serum HBV DNA by 1-2logs. The important knockdown here is that of HBsAg, an otherwise ‘undruggable’ target. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors such as entecavir are not able to meaningfully reduce HBsAg.
The discrepancy of the degrees of HBsAg and HBeAg/HBV DNA knockdowns is likely explained by the prolonged half-life of HBsAg. Repeat dosing for an extended period of time should lead to even further reductions in HBsAg. Moreover, the treated chimpanzee was an unusually tough challenge, because old (HBV for over 35 years alone), heavy and with extremely high viremia (>10exp10 genomes per ml).
Importantly, as predicted by the HBsAg knockdown-immune reactivation hypothesis, there was an apparent T cell-mediated anti-HBsAg immune response shortly after peak HBsAg knockdown levels were reached. The peak HBsAG knockdown occurred somewhere between ~days 25 and 38 and there was a flare-up in liver enzymes around day 43.
A liver-enzyme flare-up would be expected when anti-HBsAg cytotoxic T-cells start to attack HBV-infected hepatocytes. Consistent with it being due to a T-cell response, markers of T cell activation, most notably interferon gamma, were also up-regulated around the time of the flare-up. Interestingly, liver enzyme levels did not fully revert back to normal, but remained somewhat elevated compared to base-line suggesting that the RNAi knockdown kicked into gear a more persistent immune response.
Such delayed dynamics are consistent with what is seen following successful treatment with interferons. In the ~5-10% of cases where interferons are able to achieve the gold standard HBsAg elimination (in the presence of absence of HBsAg seroconversion), the elimination usually occurs after the ~52 week course of interferon, in many cases years afterwards.
Of course, the present chimpanzee data do not show an elimination of HBsAg. While I do not exclude the possibility that Arrowhead Research will come back in another 3 months or so to report that the immune system has finally overcome HBsAg, I prefer to keep expectations for such an event low and instead consider the present data as a nice starting point that indeed ARC520 is able rekindle the desired immune response after only two doses over 14 days.
Why it is unlikely to be a non-specific immune response
It is very important here to emphasize that what we are seeing here was not due to a non-specific innate immune response triggered by an immunostimulatory RNAi agent. Similarly, some RNAi delivery strategies run the risk of causing direct damage to hepatocytes which would also manifest itself by increases in liver enzymes.
The most convincing argument to me is in the timing of the flare-up and cytokine elevations. While non-specific responses usually occur in the hours and days immediately following RNAi administration, in this case, they occurred 3-5 weeks after the second dose.
Consistent with a ‘clean’ safety profile of ARC520, no such liver enzyme and cytokine elevations were seen in the phase I volunteer study for which Arrowhead reported initial safety data a month ago(2mg/kg highest dose in that study). Nevertheless, as those data only focused on the safety in the first few days following drug administration for the above reasons and the 30-day follow-up still remains to be reported, one formally cannot exclude the possibility that the unique DPC chemistry is associated with liver damage and the like only weeks after drug administration. I consider this quite unlikely though.
Going along with this theme, I expect the phase IIa study which will involve infected patients in Hong Kong and is scheduled to initiate enrollment in early 2014 to be ARC520 on top of an RT inhibitor such as entecavir. As RT inhibitors stabilize the liver of HepB patients and in light of the phase I data, any flare-ups that would be seen in that single-dose study would presumably be the result of HBsAg-specific immune reactivation.
Lots of exciting catalysts ahead over the next 6 months and who knows, due to intrapatient variability, maybe there will be a cure or two in the phase IIa study already.
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-16 15:38
2013年11月4日(星期一)
ARC520慢性乙肝疫苗:免疫系统...它复活了!
通常情况下,免疫刺激表现类似流感的症状,像的东西,你不想看到的RNAi治疗。尽管如此,有设置要在其中看到的免疫刺激。这也是用于治疗慢性HBV与HBsAg的拦截的方法的情况下。
ARC520是领先的候选人在这方面的努力和昨天的赞助商,慈姑研究,提出了非常令人振奋的数据,在慢性感染的黑猩猩已与RNA干扰剂处理。这些数据不仅是令人兴奋,因为他们大概代表减少最快的HBsAg抗原见过一个真正的感染(注:只黑猩猩被认为是反映人类HBV感染) ,没有什么是更令人兴奋的是,数据是与HBsAg特异性的T细胞的免疫反应相一致。
HBsAg的击倒的方法用于治疗慢性HBV铰链上的假设,即通过撞倒乙肝表面抗原,它或许可以重新激活人体的适应性免疫应答对病毒的成功,在我的脑海里的数据是最大的风险事件ARC520的发展。
的数据
慈姑研究于2013年在华盛顿特区的美国肝病学会肝脏会议,提出了更详细的数据被视为ARC520黑猩猩。在此之前,我们已经知道, ARC520两种剂量( 2.0mg/kg和3.0mg/kg )间隔14天,除了能够击倒大三阳超过90 % 〜80 % ,乙肝表面抗原,血清HBV DNA由1 2logs 。这里的重要击倒,乙肝表面抗原,否则undruggable的目标。反向酶抑制剂如恩替卡韦是不能够有意义地减少乙肝表面抗原。
HBsAg和HBeAg的/ HBV DNA击倒的程度的差异的原因可能的HBsAg的半衰期延长。重复给药一段较长的时间,甚至进一步减少乙肝表面抗原。此外,处理后的黑猩猩是一个异常艰难的挑战,因为旧的( 35岁以上单独HBV ) ,很重,具有极高的病毒血症( > 10exp10基因组每毫升) 。
重要的是,作为预测的HBsAg的免疫拦截的重新激活假说,有一个明显的T细胞介导的免疫反应的抗-HBsAg后不久达到峰值HBsAg的拦截水平。峰值出现的HBsAg击倒〜 25日和38日之间的某个地方,有一个爆发43天左右的肝酶。
抗HBsAg细胞毒性T细胞时,开始攻击HBV感染的肝细胞的肝酶,将有望爆发。一致的,这是由于T细胞的反应,标记的T细胞的活化,最主要的是γ-干扰素,也上调左右的时间的喇叭形。有趣的是,肝酶水平并未完全恢复正常,但仍RNAi敲除踢成齿轮更持久的免疫反应的基线相比有所升高。
这种延迟的动态与干扰素成功治疗后的保持一致。在〜 5-10%的干扰素的情况下,能够实现的黄金标准的HBsAg消除( HBsAg血清转换的情况下的存在下) ,消除通常发生〜52周的过程中干扰素后,在许多情况下,年后。
当然,本黑猩猩数据不显示一个消除对HBsAg 。虽然我不排除这种可能性,慈姑研究会回来再过3个月左右的报告,免疫系统终于攻克乙肝表面抗原,我宁愿保持这样低的事件的期望,作为一个很好的起点,而不是考虑目前的数据点确实ARC520能够重燃理想的免疫反应后,只有两个剂量超过14天。
为什么它是不太可能是一种非特异性免疫反应的
这是非常重要的,这里强调的是,我们在这里看到的是,由于非特定的先天免疫反应所引发的免疫RNA干扰剂。同样,一些RNAi提供战略运行造成直接损害肝细胞也表现本身肝酶增加的风险。
耀斑和细胞因子升高的时机对我来说是最有说服力的论据。虽然非特异性的反应通常发生在紧随RNA干扰( RNAi )给药的时间和天数,在这种情况下,发生第二次给药后3-5周。
符合ARC520一个“干净”的安全性,没有这样的肝酶和细胞因子升高被认为在研究阶段,我的志愿箭头报告的初步安全数据一个月前(在这项研究中的最高剂量为2mg/kg ) 。然而,作为这些数据只集中在安全上的第一几个天药物管理的上述理由,并在30日遵循的高达仍保持予以报道后,正式不排除可能性,独特的DPC化学的相关与肝损伤及给药后只喜欢周。我认为这不太可能,但。
随着这个主题,我希望这将涉及在香港受感染的患者,并计划在2014年初开始招生ARC520之上的RT抑制剂如恩替卡韦的IIa期研究。由于逆转录酶抑制剂平抑肝乙肝患者相I数据,任何耀斑起坐,单剂量研究中,将被视为大概是由于HBsAg特异性免疫激活。
很多令人兴奋的催化剂,在未来6个月之前,谁知道,由于药物治疗前,后组内变异,也许会有两个阶段IIa研究治愈或已。
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-16 16:19
 好文章,exciting。
好文章,exciting。
作者: 齐欢畅2 时间: 2013-11-16 16:37
期待更多香港二期实验的消息,不知是否有战友可以打听下。
作者: StephenW 时间: 2013-11-16 16:42
本帖最后由 StephenW 于 2013-11-16 16:42 编辑
回复 齐欢畅2 的帖子
请记住,博客是一个Arrowhead投资者和他不是乙肝专家.
希望他是对的.
| 欢迎光临 肝胆相照论坛 (http://hbvhbv.info/forum/) |
Powered by Discuz! X1.5 |


 NA_intercalation.jpeg]
NA_intercalation.jpeg] [/url]
[/url] NA_intercalation.jpeg]
NA_intercalation.jpeg]![]() [/url]
[/url]
 Usually, immune stimulation which manifest itself as flu-like symptoms and the like is something that you do not want to see with an RNAi Therapeutic. Having said that, there are settings in which you want to see immune stimulations. This is also the case for the treatment of chronic HBV with a HBsAg knockdown approach.
Usually, immune stimulation which manifest itself as flu-like symptoms and the like is something that you do not want to see with an RNAi Therapeutic. Having said that, there are settings in which you want to see immune stimulations. This is also the case for the treatment of chronic HBV with a HBsAg knockdown approach.  好文章,exciting。
好文章,exciting。